Do you know What is Marijuanas Plants? Definitely you knew it but now i will add some specific addition to your knowledge through this blog post.
Marijuana plants have been a subject of fascination and controversy for centuries. With increasing interest in their medicinal properties and legalization in various regions, understanding these plants has never been more important.
This article provides an in-depth look into what marijuana plants are, their effects, their place in the plant kingdom, and the best soil practices for cultivating them.
What is Marijuanas Plants: Botanical Classification
Marijuana plants belong to the Cannabis genus, classified botanically as Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis. These species are known for producing cannabinoids, compounds that can affect the human nervous system and are used medically or recreationally.
Family Name: Cannabaceae
Marijuana plants belong to the Cannabaceae family, a small group of flowering plants. This family also includes hops (Humulus lupulus), which are used in brewing beer.
The Cannabaceae family is characterized by its unique flowering structures and chemical compounds.
Species of Cannabis
There are three primary species of marijuana plants:
- Cannabis Sativa
- Characteristics: Tall growth, narrow leaves.
- Growth Patterns: Prefers warmer climates with long growing seasons.
- Cannabis Indica
- Distinct Features: Shorter stature, broad leaves.
- Cultivation: Thrives in cooler climates with shorter growing seasons.
- Cannabis Ruderalis
- Unique Attributes: Small size, early flowering.
- Uses: Often used in crossbreeding for its auto-flowering trait.
- Discover the key differences between Sativa vs. Indica, including their effects, growth patterns, and best uses for relaxation or energy.
Anatomy of the Marijuana Plant
- Leaves: Typically serrated and can vary in width.
- Stems: Support the plant structure.
- Flowers: Contain the highest concentration of cannabinoids.
- Trichomes: Tiny hair-like structures that produce cannabinoids like THC and Cannabis.
Effects of Marijuana Plants
Marijuana plants produce chemical compounds known as cannabinoids, which interact with the human body’s endocannabinoid system.

Psychoactive Components
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- Psychoactive Effects: Responsible for the “high” sensation.
- Potency: Varies between different strains.
- Cannabidiol (Cannabis)
- Therapeutic Properties: May help with anxiety, pain, and inflammation.
- Non-Psychoactive: Does not produce a “high.”
- If you’re interested in learning more about how these two components differ, check out our article on THC vs. Cannabis: A Detailed Comparison, where we break down their effects, uses, and differences.
Short-Term Effects
- Altered Senses: Changes in perception, such as seeing brighter colors.
- Mood Changes: Feelings of euphoria or relaxation.
- Cognitive Impact: Difficulty with thinking, problem-solving, and memory.
Long-Term Effects
- Memory and Cognition: Potential impact on brain development, especially in younger users.
- Physical Health: Can affect respiratory health if smoked.
Medical Applications
The use of certain plants and compounds in medical treatments has gained significant attention over the years due to their potential health benefits. These applications span a wide range of conditions, and ongoing research is helping to uncover more about their therapeutic properties.
Pain Management
One of the most prominent medical applications is in pain management, particularly for individuals suffering from chronic pain.
Chronic pain can result from a variety of conditions, including arthritis, neuropathy, and injury, and can significantly impair an individual’s quality of life.
Certain compounds, especially those derived from natural sources, have been found to potentially alleviate this pain by interacting with the body’s nervous system and reducing inflammation.
Unlike traditional pain medications, which often carry a risk of addiction or severe side effects, these alternatives are increasingly seen as a less risky option for managing persistent pain.
Specific Conditions
In addition to general pain relief, several specific medical conditions have shown promising responses to treatment using natural compounds.
- Epilepsy: Some compounds have been used in treating epilepsy, particularly in cases where traditional anti-seizure medications have proven ineffective. In some instances, these treatments have led to a significant reduction in the frequency and severity of seizures, providing a much-needed alternative for patients with drug-resistant epilepsy.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Multiple sclerosis is a debilitating neurological condition that can cause muscle spasms, pain, and difficulty with movement. Some treatments derived from natural sources have been found to help alleviate muscle stiffness and spasms, offering relief to patients who may not respond well to conventional therapies.
- Nausea from Chemotherapy: Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy often experience severe nausea and vomiting as side effects of the treatment. Certain natural compounds have been utilized to reduce nausea and improve appetite, making the treatment process more tolerable for these patients.
Research and Future Potential
While the medical applications mentioned above show promising results, it’s important to note that research is still ongoing.
The medicinal properties of these natural compounds are not yet fully understood, and more clinical trials and studies are needed to determine their long-term efficacy and safety.
Researchers are exploring various applications, such as their potential use in treating anxiety, depression, and other neurological disorders, as well as their ability to provide relief for inflammatory diseases.
As scientific understanding deepens, it is likely that the scope of medical applications will expand, offering new opportunities for treatment across a wide spectrum of health conditions.
The potential to develop alternative treatments that are more effective, less addictive, and have fewer side effects makes this an exciting area of ongoing research.
Ideal Soil Conditions for Marijuana Plants
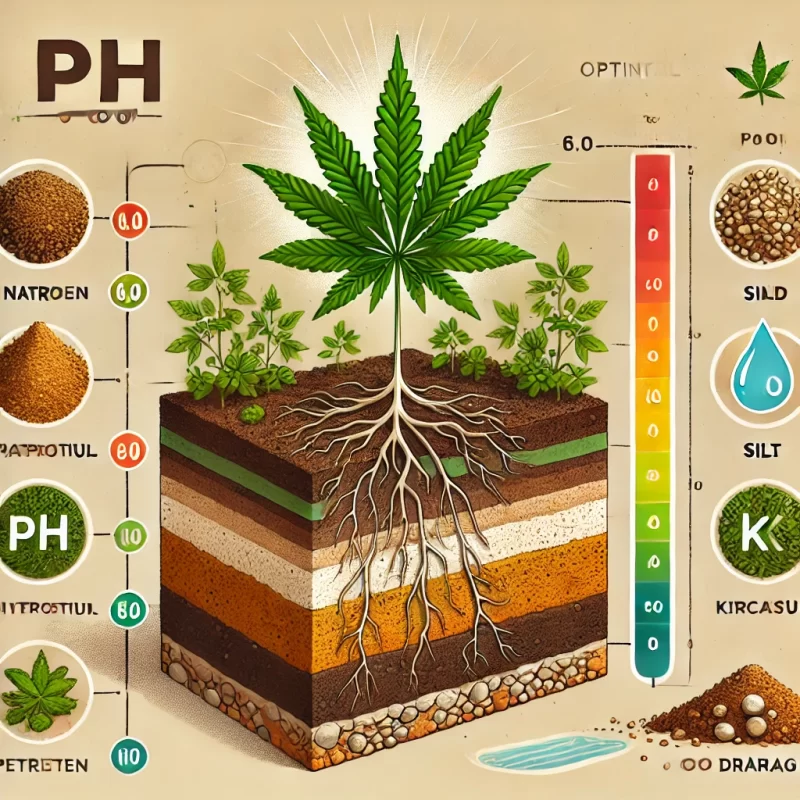
Proper soil conditions are important for the healthy growth of marijuana plants.
Importance of Soil Quality
- Plant Health: Soil provides essential nutrients.
- Yield: High-quality soil can increase the potency and quantity of the harvest.
Optimal Soil Characteristics
1. Texture
- Loamy Soil: Ideal mix of sand, silt, and clay.
- Benefits: Good drainage and nutrient retention.
2. pH Levels
- Ideal Range: Between 6.0 and 7.0.
- Nutrient Absorption: pH affects the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients.
3. Nutrient Content
- Macronutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K).
- Micronutrients: Calcium, magnesium, sulfur, and others.
Table 1: Essential Nutrients for Marijuana Plants
| Nutrient | Role in Plant Growth |
| Nitrogen (N) | Leaf development and chlorophyll production |
| Phosphorus (P) | Root growth and flower development |
| Potassium (K) | Overall plant health and disease resistance |
4. Drainage and Aeration
- Preventing Root Rot: Soil should not retain excessive water.
- Oxygen Supply: Roots need air pockets in the soil.
Soil Enhancements
- Organic Matter: Adding compost or humus enriches the soil.
- Mycorrhizal Fungi: Beneficial fungi that improve nutrient uptake.
Common Soil Types and Amendments
- Pre-made Soil Mixes: Available specifically for marijuana cultivation.
- Adjusting Soil Properties: Use perlite for aeration or peat moss for moisture retention.
Table 2: Soil Amendments and Their Benefits
| Amendment | Benefit |
| Perlite | Improves aeration and drainage |
| Vermiculite | Enhances moisture retention |
| Compost | Adds organic nutrients |
| Lime | Raises soil pH |
| Sulfur | Lowers soil pH |
Environmental and Legal Considerations
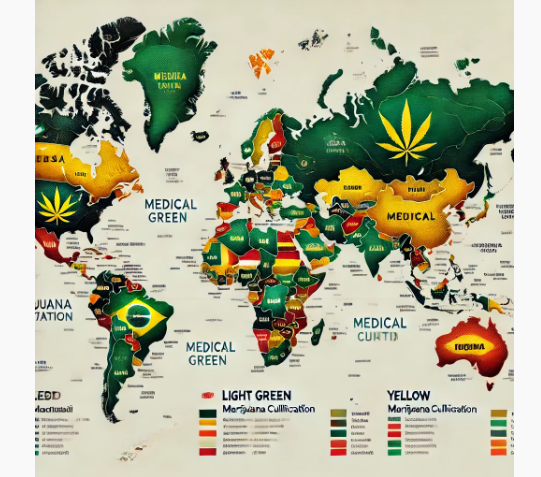
Legal Status of Cultivation
The legal framework surrounding cultivation varies significantly across different regions and countries.
It is important to recognize that no universal set of rules applies globally; instead, local governments enforce specific laws that dictate whether and how cultivation activities can take place.
These regulations may cover the type of crops that can be grown, the conditions under which they are cultivated, and the scale of production permitted.
Compliance
Before engaging in any cultivation activities, it is essential to consult and adhere to the relevant legal guidelines in your jurisdiction.
Non-compliance can lead to legal penalties, including fines or operational shutdowns. Understanding local laws not only ensures a lawful operation but also fosters a responsible and sustainable approach to agricultural practices.
Sustainable and Responsible Cultivation
In addition to legal compliance, cultivators must consider the environmental and ethical implications of their activities. Sustainable cultivation practices help mitigate the negative impact on ecosystems and natural resources, ensuring long-term viability for future generations.
Environmental Impact
One of the most critical aspects of sustainable cultivation is managing the environmental footprint. Key factors to consider include water usage and the application of pesticides.
Overuse of water resources can lead to depletion, while irresponsible pesticide use can cause soil degradation, harm to non-target organisms, and water pollution.
Implementing water-saving techniques and opting for organic or eco-friendly pesticides can greatly reduce environmental harm.
Ethical Practices
Sustainable cultivation goes beyond environmental impact—it also encompasses ethical considerations.
Cultivators should aim to optimize resource use and energy efficiency, ensuring that their operations do not exploit natural resources unnecessarily.
Responsible cultivation also means minimizing waste, reducing carbon emissions, and maintaining soil health through regenerative agricultural practices.
By adhering to both legal and environmental standards, cultivators can achieve a balance between productivity and responsibility, contributing positively to both the community and the environment.
Graph 1: Legal Status of Marijuana Cultivation Worldwide
Conclusion
Understanding marijuana plants involves exploring their botanical background, effects on the human body, and the best practices for cultivation. By focusing on optimal soil conditions and being aware of legal considerations, growers can cultivate healthy plants responsibly.

